Advanced High Strength Steel Application Guidelines: Online, Expanded and Updated
October 1, 2021Comments
WorldAutoSteel, a consortium of leading global sheet-steel producers, has a long history of promoting products and techniques that allow for their optimized use in automotive-body structures. Nearly 30 years ago, the consortium acknowledged that its automotive-industry customers were facing the conflicting challenges of reduced weight for improved emissions and fuel-economy performance while meeting ever-increasing safety regulations, all while producing a cost-effective body structure. New grades of steel helped attack these challenges, but these grades had different forming, joining and processing characteristics than the mild steels commonly processed at most companies.
This realization led to the launch of the Ultralight Steel Auto Body (ULSAB) program to demonstrate a lightweight steel auto-body structure that met a wide range of safety and performance criteria. Following ULSAB were projects that highlighted closures and suspensions, as well as other vehicle parts and systems.
Complementing these vehicle developments was the 2003 initial publication of the Advanced High Strength Steel (AHSS) Application Guidelines, which showcased global best practices on how to form and join advanced steel grades. By the 2014 release of Version 5, the AHSS Application Guidelines contained a portfolio of 50 different commercially available automotive steels. The 2017 release of Version 6 highlighted 38 unique AHSS grades alone. Dr. Stuart Keeler, the esteemed industry pioneer and former Science of Forming columnist for MetalForming magazine, served as technical editor for metallurgy/forming through the 6th release; I took this role over for the 7th version, released earlier this year.
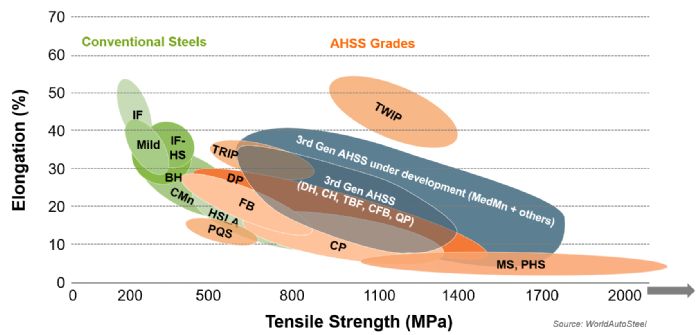 The latest version is available for free public use as a mobile-friendly online database (AHSSinsights.org) where users can browse and search to quickly find specific information of interest. The new online format enables timely updates to keep pace with the development of new technology and grades. Currently, the website includes some 150 articles with 1000 citations, many of which have links back to the original sources. Content divides into three primary sections: metallurgy, forming and joining. In addition, the website houses the AHSS Insights technical blog.
The latest version is available for free public use as a mobile-friendly online database (AHSSinsights.org) where users can browse and search to quickly find specific information of interest. The new online format enables timely updates to keep pace with the development of new technology and grades. Currently, the website includes some 150 articles with 1000 citations, many of which have links back to the original sources. Content divides into three primary sections: metallurgy, forming and joining. In addition, the website houses the AHSS Insights technical blog.









 Webinar
Webinar